Paul Sutter
Paul M. Sutter is a cosmologist at Johns Hopkins University. A prolific scientist, he has written over 60 academic publications on topics such as the earliest moments of the big bang and the largest objects in the universe. Paul is also an award-winning science communicator. He has authored three critically acclaimed, international bestselling books and has hosted television shows on Discovery, Science Channel, History Channel, and numerous digital outlets. You can find his essays in The New York Times, Scientific American, Nautilus, and more. In addition to regular appearances on NBC News, BBC News, CNN, and The Weather Channel, Paul has developed one of the most popular podcasts in the world and is a globally recognized leader in the intersection of art and science, especially in his role as a United States Cultural Ambassador.
Latest articles by Paul Sutter
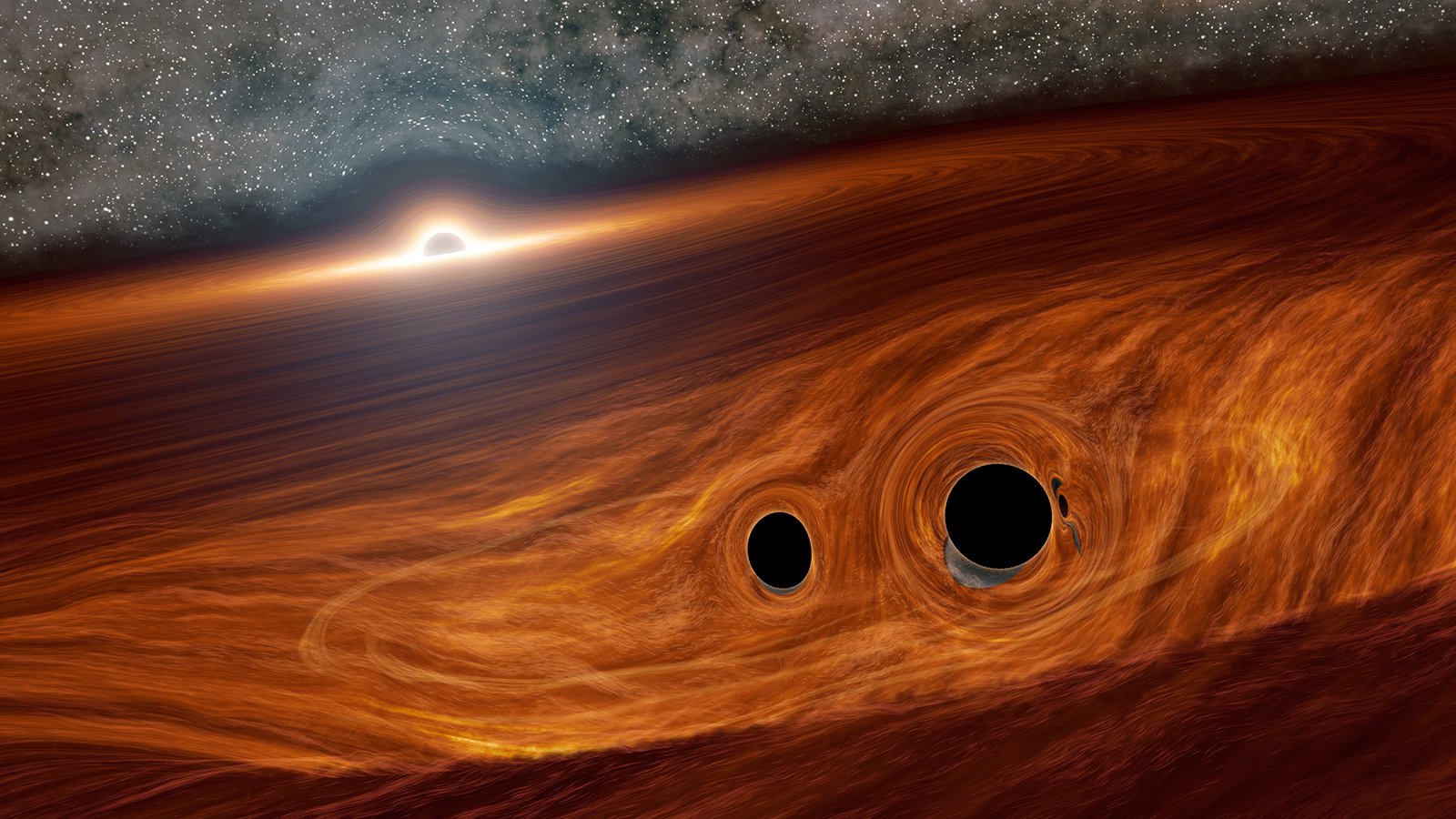

How dancing black holes get close enough to merge
By Paul Sutter published
New research suggests a way for black holes to merge quickly: They must be caught in the accretion disk of a supermassive companion.

The dark matter hypothesis isn't perfect, but the alternatives are worse
By Paul Sutter published
It's true that the dark matter hypothesis has its shortcomings — and, of course, we haven't found any dark matter particles yet. But the truth is that the alternatives are much worse.
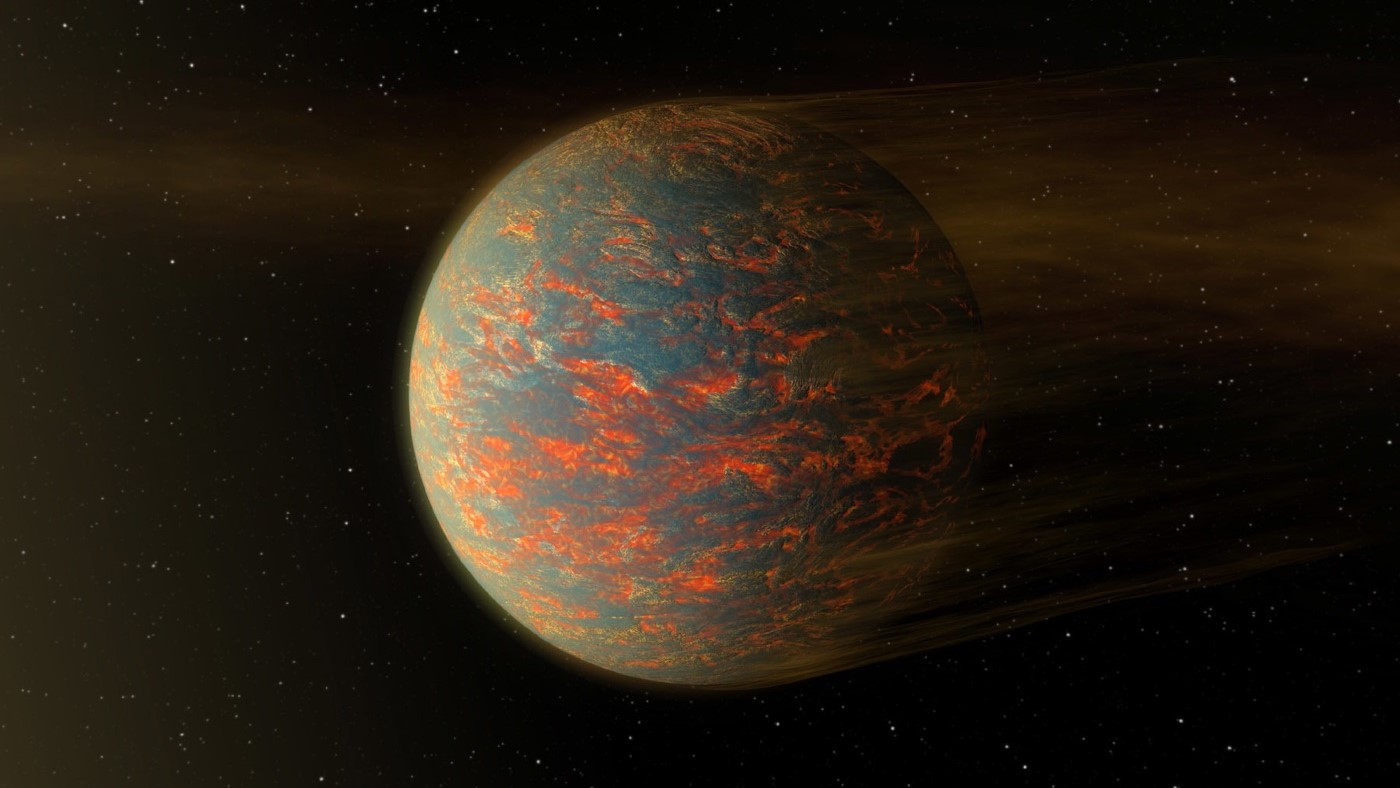

Just how big can a super-Earth get while staying 'habitable'?
By Paul Sutter published
But could these giant, rocky planets actually sustain the conditions for life? Or is life limited to smaller planets like our own?

Planets made of dark matter may have blown up, and we could see them
By Paul Sutter published
A new hypothesis proposes that a large fraction of dark matter may be bound up inside tight balls the size of Neptune — so-called dark matter planets.
Why is gravity so weak? The answer may lie in the very nature of space-time
By Paul Sutter published
Reference The solution as to why gravity is so weak may come from taking a closer look at the Higgs boson.

Radioactive decay: Discovery, process and causes
By Paul Sutter published
Reference Radioactive decay is the strange and almost mystical ability for one element to naturally and spontaneously transmute into another one.

Black holes may die differently than we thought
By Paul Sutter published
New research motivated by string theory suggests possible, and equally strange, fates for evaporating black holes.

What the Higgs Is Going on with Mass?
By Paul Sutter last updated
By now, most people have heard the refrain: "The Higgs boson creates mass." But the reality is a bit more complicated than that.

A Strange New Higgs Particle May Have Stolen the Antimatter from Our Universe
By Paul Sutter last updated
Physicists have proposed that a trio of particles called Higgs bosons could be responsible for the mysterious vanishing act of antimatter in the universe.

Physicists Search for Monstrous Higgs Particle. It Could Seal the Fate of the Universe.
By Paul Sutter last updated
Without the Higgs, the Standard Model of particle physics comes crashing down.

The Higgs Boson: A Not-So-Godlike Particle
By Paul Sutter last updated
Let's be perfectly honest: The Higgs boson and its role in the universe are not the easiest things to explain.

The Higgs boson could have kept our universe from collapsing
By Paul Sutter last updated
The Higgs boson particle could have kept our universe from collapsing within a larger multiverse, physicists say.

How black holes and galaxies play tug-of-war across the cosmos
By Paul Sutter published
How monster black holes overpower their much larger host galaxies.

Flashes from neutron star tidal waves may signal impending mergers
By Paul Sutter published
Researchers have found a new way to detect some of the most cataclysmic mergers in the universe before they happen.

Physicists link two time crystals in seemingly impossible experiment
By Paul Sutter published
Physicists have created a system of two connected time crystals, which are strange quantum systems that are stuck in an endless loop to which the normal laws of thermodynamics do not apply.
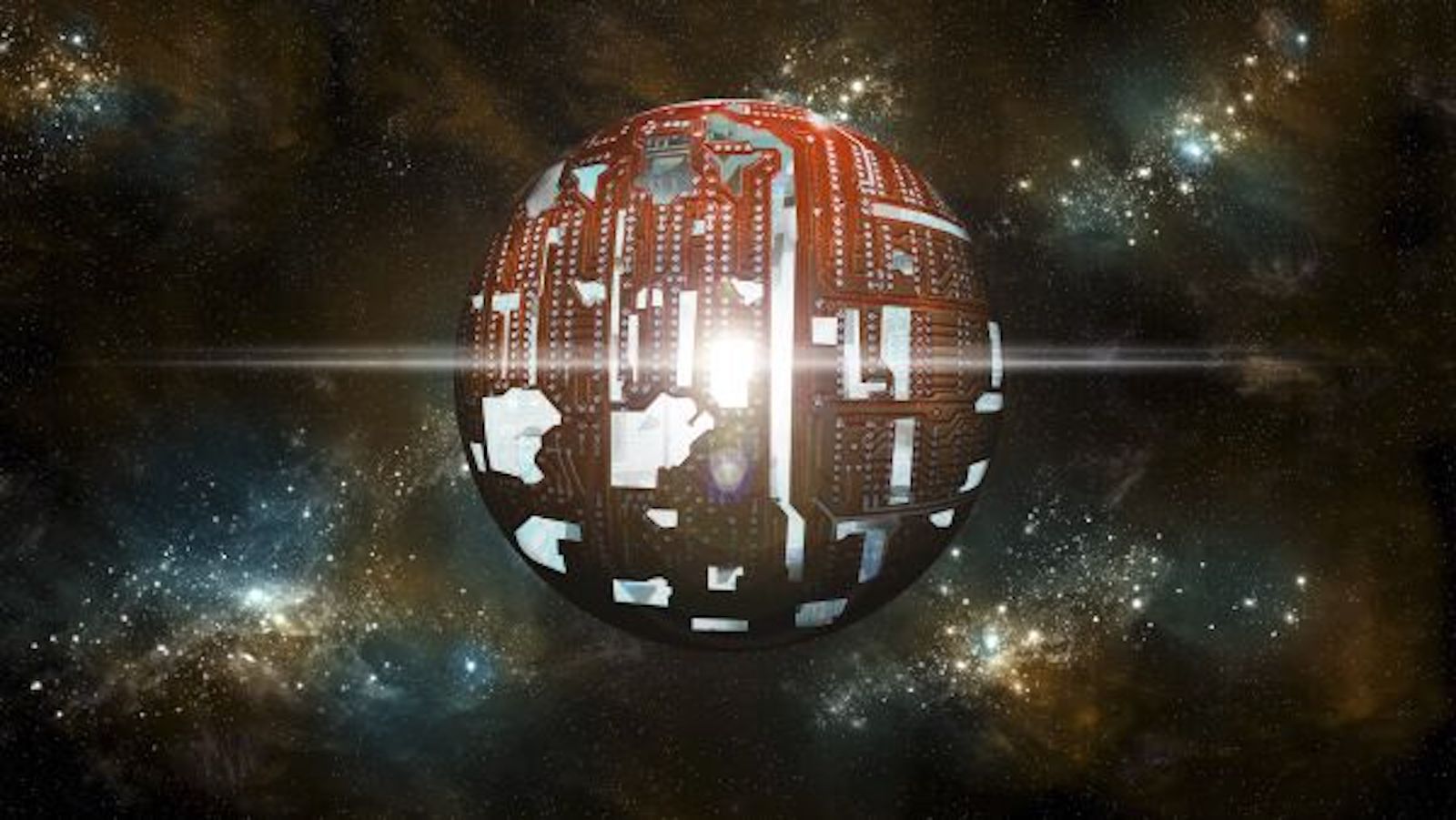

The aliens are all hanging out on Dyson spheres circling white dwarfs, physicist argues
By Paul Sutter published
If aliens exist, they do exist, they might be hanging out on Dyson spheres circling the husks of sunlike stars called white dwarfs.
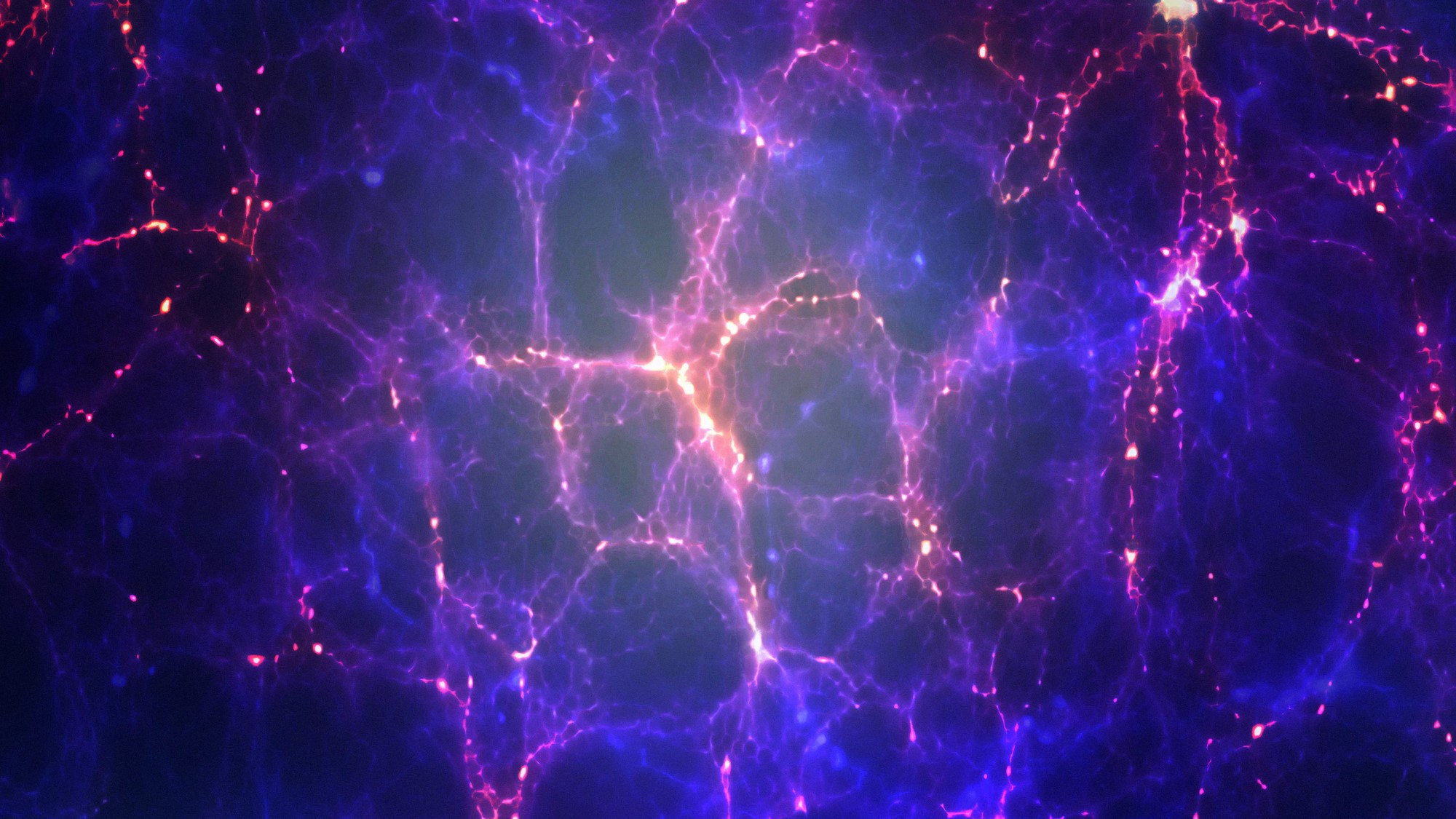

A mysterious intergalactic force is pushing against the Milky Way
By Paul Sutter published
It sounds like the premise of a bad sci-fi movie: There's some mysterious entity, beyond the boundaries of our galaxy, that is pushing against us with incredible force.
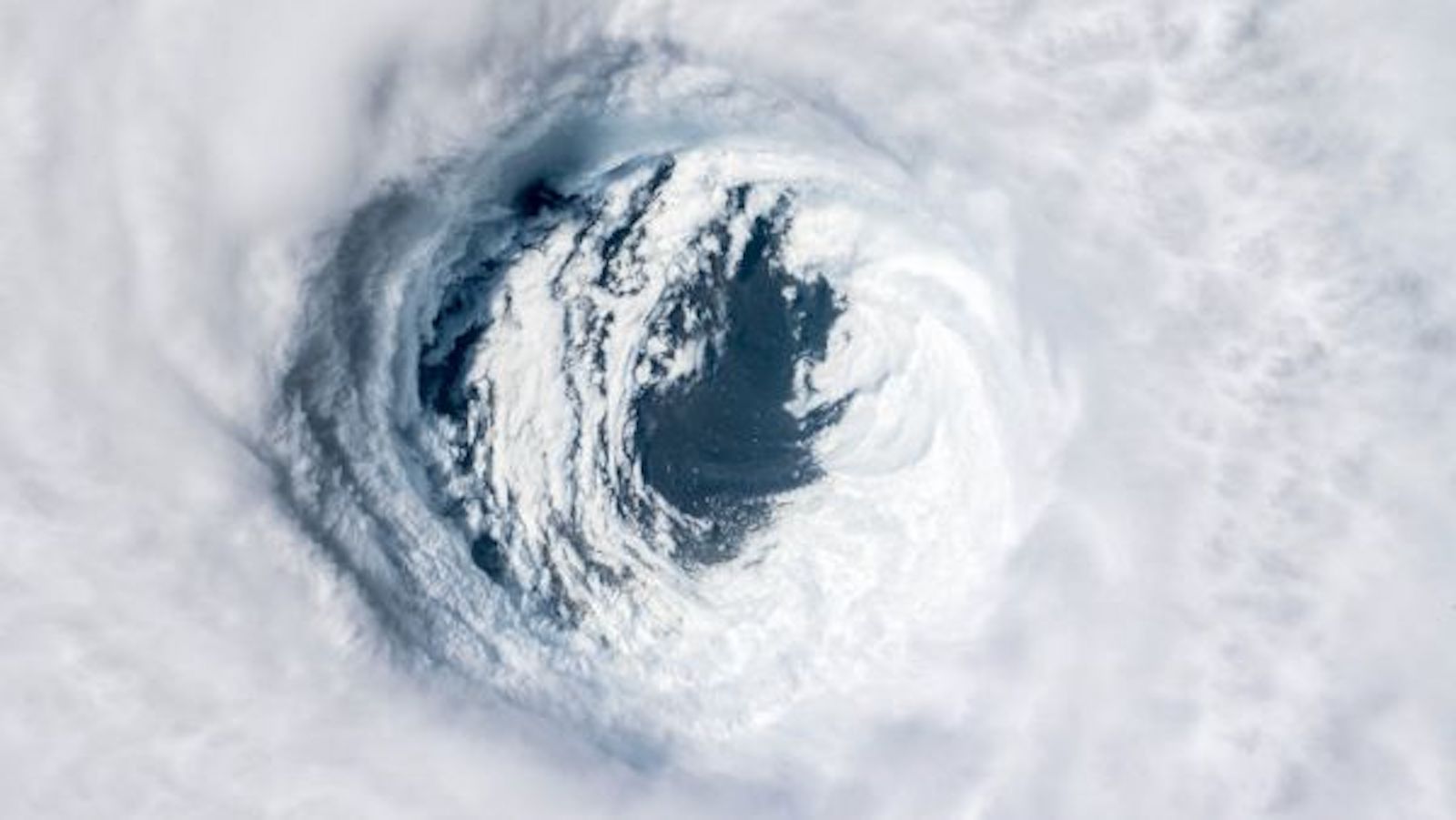

Physicists predict Earth will become a chaotic world, with dire consequences
By Paul Sutter published
Humans aren't just making Earth warmer, they are making the climate chaotic, a stark new study suggests.
Sunspots' Tangled Tale: Why the Sun Has Spots
By Paul Sutter last updated
Explaining the source of sunspots is a pretty tough nut to crack.
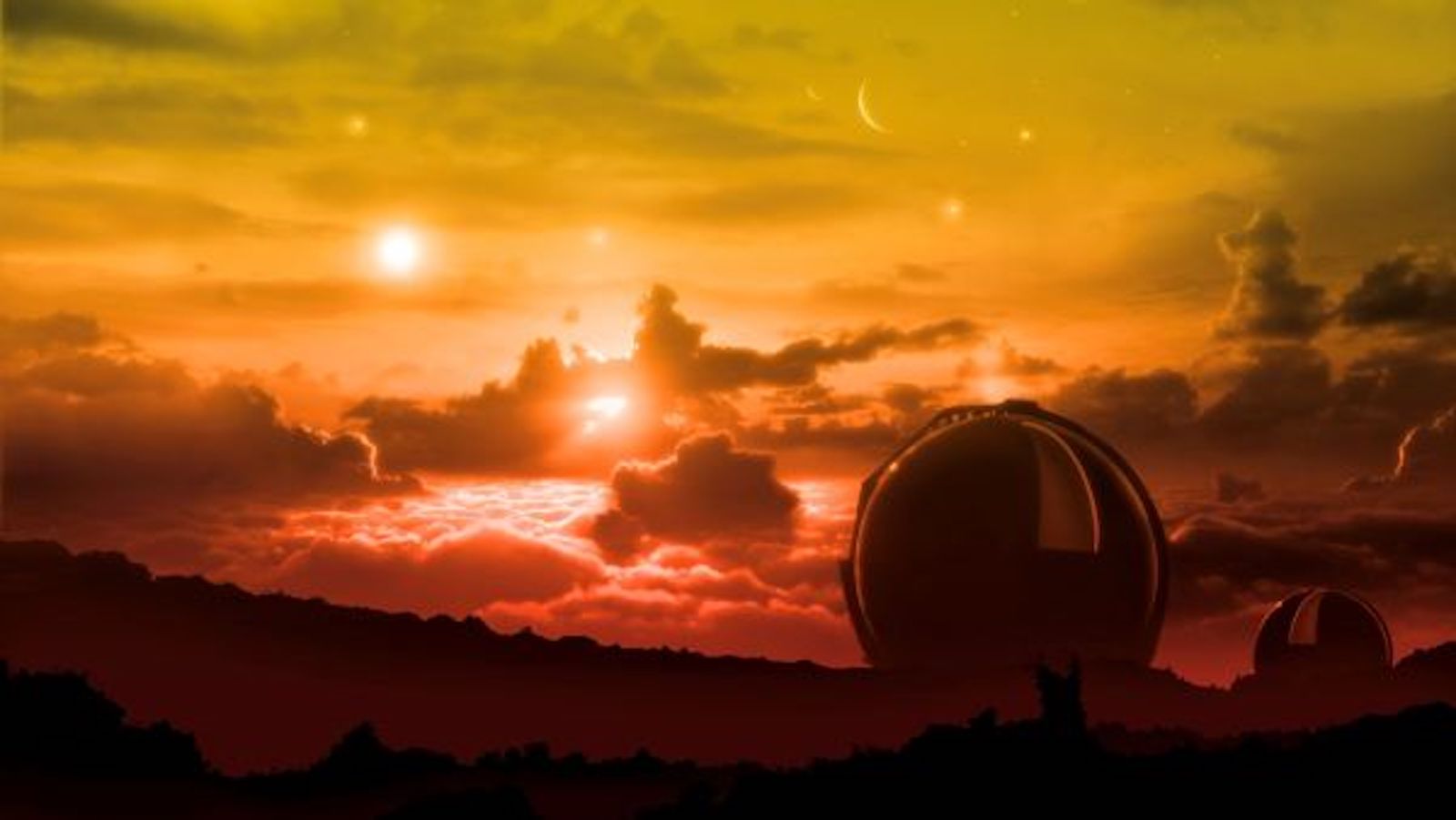

Humans could become a truly interplanetary species within 200 years, physicists claim
By Paul Sutter published
Harness renewable energy to explore the cosmos or risk planetary doom, new physics study argues.

The 'twin paradox' shows us what it really means for time to be relative
By Paul Sutter published
What goes for moving clocks goes for everything else; physics, chemistry and biology all operate at a slower pace in moving frames of reference.

Stronger gravity in the early universe may solve a cosmological conundrum
By Paul Sutter published
The inflationary epoch that caused our universe to rapidly expand in its earliest moments may be connected to the modern era of dark energy.
Venus-like worlds are surprisingly common in 'habitable' zones
By Paul Sutter published
The current definition of habitable zone only examines the amount of sunlight reaching a planet. It may be time to question that definition.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!


